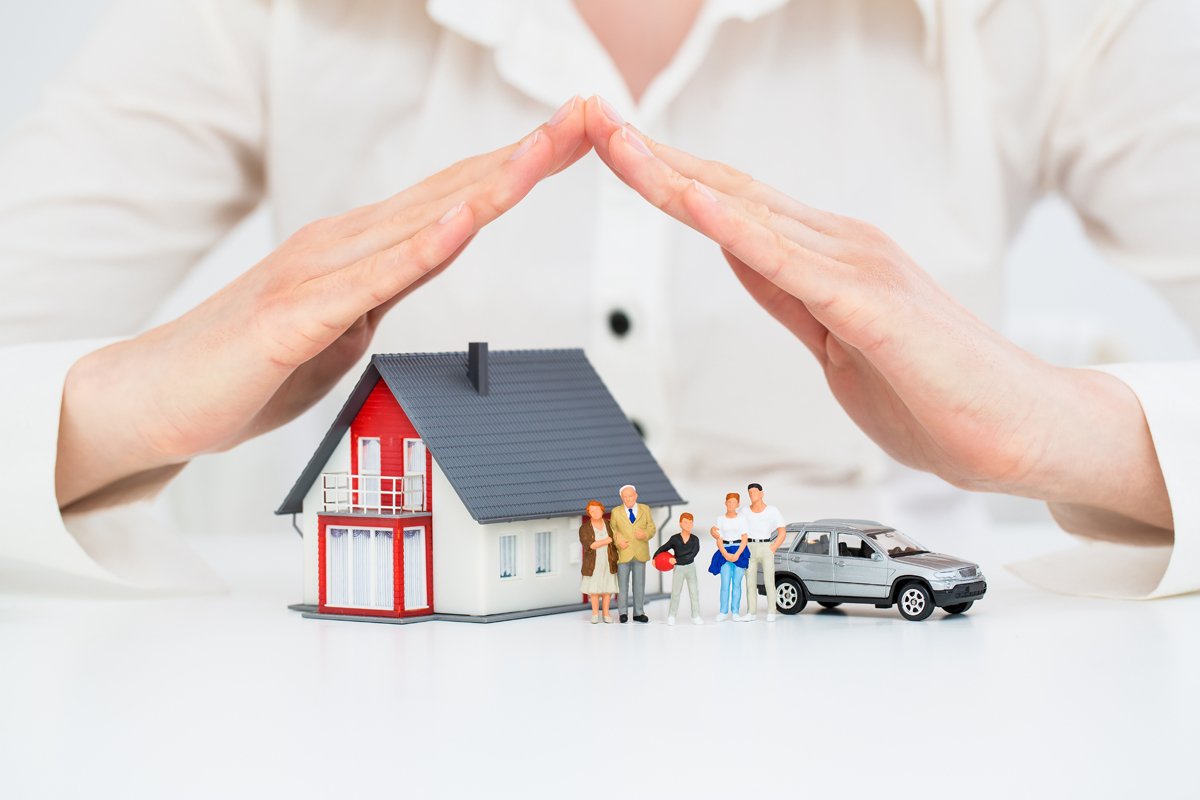
What is Insurance?
Insurance is a risk management strategy that protects individuals and businesses from financial losses due to unexpected events or accidents. It is a contractual agreement between the insured (policyholder) and the insurer (insurance company), where the insured pays a premium, and the insurer agrees to provide financial compensation or coverage in case of a covered loss.
The primary purpose of insurance is to transfer the risk of potential financial losses from the insured to the insurer. By pooling the premiums from many policyholders, insurance companies can spread the risk and pay out claims to those who experience covered losses.
History of Insurance
The concept of insurance has its origins dating back to ancient times when people realized the need to mitigate risks and share losses among a group. Early forms of insurance can be traced to the practice of merchants distributing their goods across multiple ships to minimize the potential impact of a single vessel’s loss.
One of the earliest documented instances of insurance dates back to the ancient Babylonian civilization, where traders would pay a premium to lenders to guarantee the safe arrival of their goods. This practice later evolved into maritime insurance, which became prevalent during the European Age of Exploration in the 15th and 16th centuries.
The Great Fire of London in 1666 marked a significant milestone in the development of modern insurance. The devastating fire prompted the establishment of the first fire insurance company, the “Insurance Office for Houses,” which later became the Phoenix Assurance Company.
How Insurance Works
Insurance is based on the principle of risk pooling, where many individuals or entities contribute premiums to a common fund from which claims are paid. The core idea is to spread the risk of potential losses across a large group, making the burden more manageable for each individual.
Premiums are the payments made by policyholders to the insurance company in exchange for coverage. These premiums are calculated based on various factors, such as the level of risk, the type of coverage, and the insured’s personal circumstances. Insurance companies use actuarial models and statistical data to determine the appropriate premium rates.
Deductibles are the portion of a claim that the policyholder agrees to pay out-of-pocket before the insurance coverage kicks in. Higher deductibles typically result in lower premium payments, as the policyholder assumes more financial responsibility for smaller claims.
Types of Insurance Policies
Insurance policies can be broadly categorized into different types based on the specific risks they cover. Here’s an overview of some common types of insurance policies:
Life Insurance: Life insurance provides financial protection to your beneficiaries in the event of your untimely death. It helps cover expenses like outstanding debts, mortgages, and future needs like children’s education. The two main types are term life insurance, which provides coverage for a specific period, and whole life insurance, which provides lifelong coverage.
Health Insurance: Health insurance helps cover the costs of medical expenses, including doctor visits, hospital stays, surgeries, and prescription drugs. It can be obtained through an employer, purchased individually, or provided by government programs like Medicare and Medicaid.
Auto Insurance: Auto insurance is mandatory in most states and protects you from financial liability in the event of an accident or theft involving your vehicle. It typically includes coverage for bodily injury, property damage, collision, and comprehensive protection.
Homeowners Insurance: Homeowners insurance provides coverage for your home and personal belongings against risks like fire, theft, and natural disasters. It may also include liability protection in case someone gets injured on your property.
Choosing the Right Insurance
Selecting the right insurance policy can be a daunting task, as there are numerous factors to consider. It’s crucial to strike a balance between adequate coverage and affordability. The first step is to assess your coverage needs based on your personal circumstances, assets, and potential risks. For instance, if you own a home, you’ll need homeowner’s insurance to protect your property and belongings against damages or losses.
Your budget is another essential factor to consider. Insurance premiums can vary significantly depending on the coverage limits, deductibles, and the insurer. It’s wise to shop around and compare quotes from multiple providers to find the most competitive rates. Don’t compromise on coverage just to save a few dollars, as this could leave you underinsured and vulnerable in the event of a claim.
Deductibles play a significant role in determining your premium costs. A higher deductible means you’ll pay more out-of-pocket if you file a claim, but it also results in lower premiums. Conversely, a lower deductible translates to higher premiums but less out-of-pocket expense when making a claim. It’s essential to strike a balance between the deductible amount and your ability to cover the costs in case of a claim.
Insurance Regulations and Laws
Insurance is a heavily regulated industry, with a complex web of laws and regulations at both the state and federal levels. These regulations are designed to protect consumers, ensure fair practices, and maintain the financial stability of insurance companies.
The FIO monitors the insurance industry and advises the federal government on policy issues, while the NAIC is a standard-setting organization that coordinates state-level insurance regulation.
Consumer protection laws are a critical aspect of insurance regulations. These laws aim to safeguard policyholders from unfair or deceptive practices by insurance companies. Examples include the Affordable Care Act (ACA), which established consumer protections in the health insurance market, and the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA), which regulates the use of credit reports in insurance underwriting.
Insurance Claims Process
The insurance claims process begins when you file a claim with your insurance provider after experiencing a covered loss or damage. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you navigate the process:
-
Report the Incident: Notify your insurance company as soon as possible after the incident occurs. Provide details about the loss or damage and follow any specific instructions from your insurer.
-
Gather Documentation: Collect all relevant documentation related to the claim, such as police reports, medical records, repair estimates, or receipts for damaged or lost items. Your insurer may require specific documentation, so be sure to check their requirements.
-
File the Claim: Submit your claim to the insurance company, either online, by phone, or through an agent. Provide all necessary details and documentation to support your claim.
-
Claims Investigation: The insurance company will assign a claims adjuster to investigate the incident and assess the extent of the loss or damage. The adjuster may contact you for additional information or to schedule an inspection.
-
Damage Assessment: If applicable, the claims adjuster will inspect the damaged property or conduct an investigation to determine the cause and extent of the loss. They may also consult with experts or contractors to assess the cost of repairs or replacement.
Insurance Industry Trends and Innovations
The insurance industry is undergoing a digital transformation, driven by emerging technologies and changing consumer expectations. One of the most significant trends is the rise of InsurTech, which refers to the use of technology innovations to improve and automate the insurance industry’s operations and processes.
InsurTech companies are leveraging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, blockchain, and the Internet of Things (IoT) to streamline underwriting, claims processing, and customer service.
Another notable trend is the growth of usage-based insurance (UBI), also known as pay-as-you-drive or pay-how-you-drive insurance. UBI policies use telematics technology, such as in-vehicle devices or smartphone apps, to monitor driving behavior and calculate premiums based on factors like mileage, speed, and braking patterns. This approach incentivizes safer driving habits and can result in lower premiums for low-risk drivers.
Insurance and Risk Management
Insurance plays a crucial role in risk management by providing a mechanism for transferring and mitigating risks. Risk management is the process of identifying, assessing, and controlling potential risks that could negatively impact an individual, organization, or business. Insurance serves as a tool to manage these risks effectively.
Risk assessment is a fundamental aspect of risk management. It involves analyzing and evaluating the potential risks an entity faces, considering factors such as the likelihood of occurrence and the potential impact. Insurance companies conduct thorough risk assessments to determine the appropriate premiums and coverage levels for their clients.
Risk mitigation strategies are employed to reduce or minimize the potential impact of identified risks. Insurance is a key risk mitigation strategy that allows individuals and organizations to transfer a portion of their risk to an insurance company. By paying premiums, policyholders can protect themselves from the financial consequences of covered risks, such as property damage, liability claims, or medical expenses.
Insurance Fraud and Prevention
Insurance fraud is a deliberate act of deception committed against an insurance company, involving the misrepresentation or concealment of facts to obtain financial gain. It can take various forms, such as exaggerating or fabricating claims, providing false information on applications, or staging accidents or injuries. Insurance fraud is a serious crime that can have severe consequences for both individuals and insurance companies.
Types of Insurance Fraud
-
Claims Fraud: This type of fraud involves making false or inflated claims to receive higher payouts from the insurance company. Examples include staging accidents, faking injuries, or exaggerating the extent of damages.
-
Application Fraud: This occurs when individuals provide false or misleading information on insurance applications to obtain lower premiums or coverage they would not otherwise qualify for. It may involve concealing pre-existing medical conditions, misrepresenting personal information, or understating risk factors.
-
Premium Diversion: In this case, an insurance agent or broker collects premiums from clients but fails to remit them to the insurance company, essentially pocketing the money.
-
Insurer Fraud: While less common, insurer fraud can occur when an insurance company engages in deceptive practices, such as denying legitimate claims, misrepresenting policy terms, or charging excessive premiums.
Consequences of Insurance Fraud
Insurance fraud is a serious offense that can result in severe legal and financial consequences. Depending on the severity and circumstances, individuals involved in insurance fraud may face criminal charges, fines, imprisonment, and civil lawsuits. Additionally, insurance companies may cancel policies, increase premiums, or refuse to provide coverage to individuals with a history of fraud.
Fraud Prevention Measures
Insurance companies employ various measures to prevent and detect fraud, including:
-
Data Analytics: Insurers use sophisticated data analysis techniques to identify patterns and red flags that may indicate fraudulent behavior.
-
Underwriting Processes: Rigorous underwriting processes, including background checks and verification of information provided on applications, can help identify potential fraud during the application stage.
-
Claim Investigations: Insurance companies conduct thorough investigations of suspicious claims, involving interviews, surveillance, and gathering evidence.
-
Anti-Fraud Policies: Insurers implement strict anti-fraud policies and procedures, including fraud hotlines and whistleblower programs, to encourage reporting and discourage fraudulent activities.
-
Public Awareness Campaigns: Insurance companies and regulatory bodies often launch public awareness campaigns to educate consumers about the consequences of insurance fraud and encourage reporting.
Fraud Investigation
When insurance fraud is suspected, insurers may initiate an investigation process. This typically involves gathering and analyzing evidence, conducting surveillance, interviewing witnesses, and collaborating with law enforcement agencies if necessary. Insurance investigators employ various techniques, such as background checks, financial analysis, and forensic examination, to uncover fraudulent activities.
Effective fraud prevention and investigation are crucial for maintaining the integrity of the insurance system and protecting the interests of honest policyholders. By combating insurance fraud, insurers can minimize financial losses, maintain affordable premiums, and uphold the trust of their customers.
Careers in the Insurance Industry
The insurance industry offers a wide range of career opportunities, from customer-facing roles to behind-the-scenes analytical positions. Here are some of the most common careers in the insurance industry:
Insurance Agents and Brokers
Insurance agents and brokers are the front-line representatives of insurance companies. They work directly with clients to understand their needs, assess risks, and recommend appropriate insurance policies. Agents typically represent a single insurance company, while brokers work independently and can offer policies from multiple insurers.
Underwriters
Underwriters are responsible for evaluating and analyzing the risks associated with potential insurance policies. They review applications, assess the likelihood of claims, and determine the appropriate premiums and coverage limits. Underwriters play a crucial role in ensuring the profitability and sustainability of insurance companies.
Claims Adjusters
When policyholders file claims, claims adjusters are tasked with investigating the circumstances, assessing the damages or losses, and determining the appropriate compensation based on the policy terms. They may work for insurance companies or as independent adjusters.
Actuaries
Actuaries are highly skilled professionals who use statistical analysis, mathematics, and financial theory to calculate risks and determine appropriate premium rates. They play a vital role in ensuring the financial stability of insurance companies by helping them price their products accurately and manage their risk exposure.
Customer Service Representatives
Insurance companies rely on customer service representatives to handle inquiries, process policy changes, and provide general support to policyholders. These professionals must have excellent communication skills and a thorough understanding of insurance products and processes.
Insurance Managers and Executives
Insurance companies require skilled managers and executives to oversee operations, develop strategies, and ensure compliance with regulations. These roles may include positions such as claims managers, underwriting managers, sales managers, and top-level executives like chief executive officers (CEOs) and chief financial officers (CFOs).
The insurance industry offers diverse career paths, from entry-level positions to highly specialized roles requiring advanced degrees and certifications. Opportunities exist in various sectors, including life insurance, health insurance, property and casualty insurance, and more.
Insurance and Personal Finance
Insurance plays a crucial role in personal financial planning and risk management. It provides a safety net against potential financial losses caused by unexpected events, such as accidents, illnesses, property damage, or liability claims. By incorporating insurance into your financial plan, you can protect your assets, income, and overall financial well-being.
One of the primary reasons for including insurance in your personal finance strategy is to mitigate the financial impact of unforeseen circumstances. Life is unpredictable, and even the most careful planning cannot account for every potential risk. Insurance offers a way to transfer these risks to an insurance provider, allowing you to focus on your financial goals without the constant worry of potential setbacks.
When it comes to budgeting for insurance premiums, it’s essential to strike a balance between adequate coverage and affordability. Evaluate your specific needs and risks, and prioritize the types of insurance that are most relevant to your situation. For example, if you have dependents, life insurance should be a top priority to ensure their financial security in the event of your untimely passing.